Self-adjusting antibacterial properties of Ag-incorporated nanotubes on micro-nanostructured Ti surfaces†
Abstract
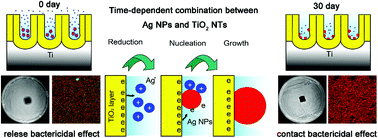
Titanium (Ti) is a widely used implant material in clinics; however, failures still frequently occur due to its bioinertness and poor antibacterial capability. Post-implant infections most likely occur within the first two weeks. Thereafter, the host immune system lowers the infection risk, and biosafety becomes the first consideration. Therefore, endowing biomedical Ti with a time-dependent bactericidal effect is of considerable interest. In this study, Ag nanoparticles (NPs) as the antibacterial agent were incorporated deeply into TiO2 nanotubes prepared on the sandblasted and etched (SLA) Ti surface. The incorporated Ag NPs were verified to automatically transform from a free state to an immobilized state, rendering the constructed platform exhibit a self-adjusting antibacterial effect. It showed strong “release bactericidal” activity in the early phase that gradually changed to the “contact bactericidal” ability. Such a smart alteration could satisfy the varied antibacterial requirements in different periods after biomaterial implantation. Moreover, the nanotubular structure could accelerate apatite formation and improve cell adhesion and proliferation when compared with those of commercially used SLA implants. Based on these results, it can be concluded that Ag-NP-incorporated micro-nanostructured Ti has worthwhile biological and time-dependent antibacterial properties, and it can have promising applications in orthopedics, dentistry, and fabrication of other biomedical devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...