Dual bioresponsive antibiotic and quorum sensing inhibitor combination nanoparticles for treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in vitro and ex vivo†
Abstract
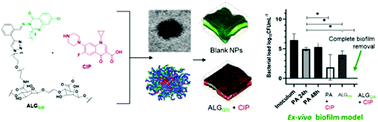
Many debilitating infections result from persistent microbial biofilms that do not respond to conventional antibiotic regimens. A potential method to treat such chronic infections is to combine agents which interfere with bacterial biofilm development together with an antibiotic in a single formulation. Here, we explore the use of a new bioresponsive polymer formulation derived from specifically modified alginate nanoparticles (NPs) in order to deliver ciprofloxacin (CIP) in combination with the quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI) 3-amino-7-chloro-2-nonylquinazolin-4(3H)-one (ACNQ) to mature Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. The alginate NPs were engineered to incorporate a pH-responsive linker between the polysaccharide backbone and the QSI, and to encapsulate CIP via charge–charge interactions of the positively-charged drug with the carboxyl residues of the alginate matrix. In this way, a dual-action release of antibiotic and QSI was designed for the low-pH regions of a biofilm, involving cleavage of the QSI-linker to the alginate matrix and reduced charge–charge interactions between CIP and the polysaccharide as the alginate carboxyl side-chains protonated. When tested in a biofilm model the concomitant release of CIP + QSI from the pH-responsive nanoparticles significantly reduced the viability of the biofilm compared with CIP treatment alone. In addition, the alginate NPs were shown to penetrate deeply into P. aeruginosa biofilms, which we attribute in part to the charges of the NPs and the release of the QSI agent. Finally, we tested the formulation in both a 2D keratinocyte and a 3D ex vivo skin infection model. The dual-action bio-responsive QSI and CIP release nanoparticles effectively cleared the infection in the latter, suggesting considerable promise for combination therapeutics which prevent biofilm formation as well as effectively killing mature P. aeruginosa biofilms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...