Development of EGFR-targeted evodiamine nanoparticles for the treatment of colorectal cancer
Abstract
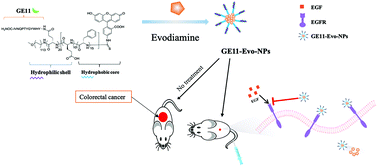
Invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer (CRC) are leading causes of death of CRC patients. Previous findings demonstrate that evodiamine (Evo), an indolequinone alkaloid, is effective in combating CRC; however, its poor aqueous solubility and low oral bioavailability limit its application in the prevention of invasion and metastasis of CRC. It is known that selectively targeting cancer-specific receptors highly expressed on the surface of cancer cells by nanocarriers loaded with cytotoxic drugs is a viable strategy in nanobiotechnology to enhance cancer cell killing and minimize side effects. In this study, we report the development of a new class of nanotherapeutics: EGFR-targeting Evo-encapsulated poly(amino acid) nanoparticles (GE11-Evo-NPs). These nanoparticles exhibited good aqueous solubility, slow release, and active targeting capability. Their inhibitory effect on human colon cancer cells and therapeutic efficacy against invasion and metastasis of CRC in nude mice were systematically investigated. Mechanisms of the GE11-Evo-NPs against EGFR mediated invasion and metastasis of CRC were also explored. Compared with free Evo, the GE11-Evo-NPs showed significantly increased cytotoxicity to colon cancer cells and potently inhibited CRC LoVo cell adhesion, invasion, and migration. The expression of EGFR, VEGF, and MMP proteins was dramatically down-regulated, which may partially account for their inhibition of invasion and metastasis of CRC. Moreover, in vivo studies show that the GE11-Evo-NPs exhibited much greater potency than other control groups in inhibiting CRC invasion and metastasis, tumor volume, and growth in nude mice, leading to a significantly prolonged tumor-bearing survival duration (P < 0.01).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...