Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes encapsulated in functional peptide hydrogels promote cardiac repair†
Abstract
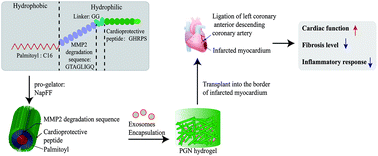
Stem cell-derived exosomes have been recognized as a potential therapy for cardiovascular disease. However, the low retention rate of exosomes after transplantation in vivo remains a major challenge in clinical applications. The aim of this study is to investigate whether human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes (UMSC-Exo) encapsulated in functional peptide hydrogels could increase the retention and stability of exosomes and improve heart function in a rat myocardial infarction model. Our results demonstrated that the PA-GHRPS peptide protected H9C2 cells from H2O2-induced oxidative stress. The gelatinization ability of PA-GHRPS can be enhanced by peptide NapFF. Therefore, these two peptides were mixed to form the PGN hydrogel, which was used to encapsulate exosomes. Our data showed that the PGN hydrogel was able to encapsulate exosomes effectively and ensured a stable and sustained release of exosomes. The exosome/PGN hydrogel mixture was injected into the infarcted border zone of rat hearts. Compared to the exosome treatment alone, the mixture improved the myocardial function by reducing inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis, and by promoting angiogenesis. The strategy used in this study provided a practical and effective method to harness exosomes for myocardial regeneration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...