Regenerating infected bone defects with osteocompatible microspheres possessing antibacterial activity†
Abstract
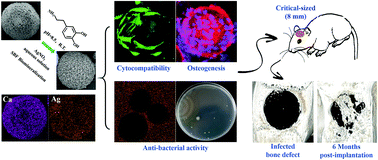
Treatment of infected bone defects still remains a formidable clinical challenge, and the design of bone implants with both anti-bacterial activity and -osteogenesis effects is nowadays regarded as a powerful strategy for infection control and bone healing. In the present study, bioresorbable porous-structured microspheres were fabricated from an amphiphilic block copolymer composed of poly(L-lactide) and poly(ethyl glycol) blocks. After being surface coated with mussel-inspired polydopamine, the microspheres were loaded with nanosilver via the reduction of silver nitrate and apatite via biomineralization in sequence. At optimized loading amounts, the nanosilver-loaded microspheres showed no unfavorable effects on the proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells despite preserving strong antibacterial activity in in vitro evaluations. For the critical-sized defects (ϕ = 8 mm) in the rat cranium that was pre-infected with Staphylococcus aureus, the filling of the dual-purpose microspheres demonstrated an effective way to kill bacteria in vivo, and in the meantime, it promoted new bone formation efficiently alongside the degradation of microspheres. Thus, the results suggested that bioresorbable microspheres with both osteoconductive and antibacterial activities were a good choice for treating infected bone defects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...