Reduction/photo dual-responsive polymeric prodrug nanoparticles for programmed siRNA and doxorubicin delivery†
Abstract
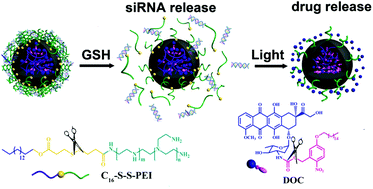
Dual and multi-stimuli responsive polymeric nanoparticles that respond to two or more signals can further improve drug release performance compared with nanoparticles that respond to a single stimulus. However, usage of such nanoparticles to deliver siRNA and chemotherapeutic drugs in a sequential manner are currently very rare; meanwhile, this technology is vital to optimize the efficacy of chemotherapy towards cancer cells with multidrug resistance. By loading o-nitrobenzyl ester derivative caged DOX (DOC) into the inner poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) core and adsorbing siRNA of P-gp protein onto the cationic polymeric shell derived from a disulfide-containing alkyl modified polyethylenimine (C16-S-S-PEI), here, a reduction/photo dual responsive device (RPDRD) is successfully designed for programmed P-gp siRNA and doxorubicin delivery. The dual-stimuli design of the RPDRD allows tumor microenvironment-specific and rapid release of P-gp siRNA triggered by the enrichment of reducing agent glutathione (GSH, up to 10 mM) for reversal of drug resistance by initially suppressing P-gp protein expression in MCF/ADR cells and then selectively triggering drug release by external light for chemotherapy afterwards. The sequential release behavior of P-gp siRNA and DOX can be demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo, thus enhancing the intracellular drug retention and optimizing the chemotherapy efficacy of DOX by silencing P-gp; this strategy may have extensive application prospects in MDR cancer treatment in future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...