Engineering of hemocompatible and antifouling polyethersulfone membranes by blending with heparin-mimicking microgels†
Abstract
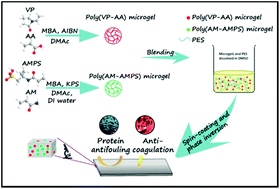
To improve the hemocompatibility and antifouling property of polyethersulfone (PES) membranes, heparin-mimicking microgels of poly(acrylic acid-co-N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) (P(AA-VP)) and poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid-co-acrylamide) (P(AMPS-AM)) were synthesized by conventional free radical copolymerization, and then incorporated into a PES matrix by blending. The results of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) confirmed that heparin-mimicking microgels were successfully synthesized. The presence of the microgels in the membrane matrix was also confirmed by attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and SEM. Compared with pristine PES membranes, the improvement of the antifouling property of the heparin-mimicking microgel modified membranes was demonstrated by the increased flux recovery ratio and improved anti-bacterial adhesion, while the enhancement of hemocompatibility for the modified membranes was proved by the decreased plasma protein adsorption, suppressed platelet adhesion, prolonged clotting times, as well as depressed blood-related complement activation. Additionally, after introducing the heparin-mimicking microgels, the membranes showed enhanced cell adhesion and proliferation properties. These results indicated that the heparin-mimicking microgel modified membranes had great potential to be used as blood contacting materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...