Chemically modified inulin microparticles serving dual function as a protein antigen delivery vehicle and immunostimulatory adjuvant†
Abstract
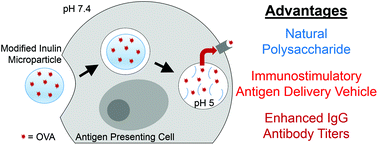
To develop a new subunit vaccine adjuvant, we chemically modified a naturally-occurring, immunostimulatory inulin polysaccharide to produce an acid-sensitive biopolymer (acetalated inulin, Ace-IN). Various hydrophobic Ace-IN polymers were formed into microparticles (MPs) by oil-in-water emulsions followed by solvent evaporation These Ace-IN MPs possessed tunable degradation characteristics that, unlike polyesters used in FDA-approved microparticulate formulations, had only pH-neutral hydrolytic byproducts. Macrophages were passively targeted with cytocompatible Ace-IN MPs. TNF-α production by macrophages treated with Ace-IN MPs could be altered by adjusting the polymers’ chemistry. Mice immunized with Ace-IN MPs encapsulating a model ovalbumin (OVA) antigen showed higher production of anti-OVA IgG antibody levels relative to soluble antigen. The antibody titers were also comparable to an alum-based formulation. This proof-of-concept establishes the potential for chemically-modified inulin MPs to simultaneously enable dual functionality as a stimuli-controlled antigen delivery vehicle and immunostimulatory adjuvant.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...