Dual-stage growth factor release within 3D protein-engineered hydrogel niches promotes adipogenesis†
Abstract
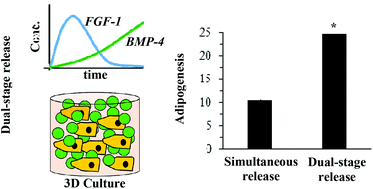
Engineered biomimetic microenvironments from hydrogels are an emerging strategy to achieve lineage-specific differentiation in vitro. In addition to recapitulating critical matrix cues found in the native three-dimensional (3D) niche, the hydrogel can also be designed to deliver soluble factors that are present within the native inductive microenvironment. We demonstrate a versatile materials approach for the dual-stage delivery of multiple soluble factors within a 3D hydrogel to induce adipogenesis. We use a mixing-induced two-component hydrogel (MITCH) embedded with alginate microgels to deliver two pro-adipogenic soluble factors, fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF-1) and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4) with two distinct delivery profiles. We show that dual-stage delivery of FGF-1 and BMP-4 to human adipose-derived stromal cells (hADSCs) significantly increases lipid accumulation compared with the simultaneous delivery of both growth factors together. Furthermore, dual-stage growth factor delivery within a 3D hydrogel resulted in substantially more lipid accumulation compared to identical delivery profiles in 2D cultures. Gene expression analysis shows upregulation of key adipogenic markers indicative of brown-like adipocytes. These data suggest that dual-stage release of FGF-1 and BMP-4 within 3D microenvironments can promote the in vitro development of mature adipocytes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...