The bioactivity of composite Fmoc-RGDS-collagen gels
Abstract
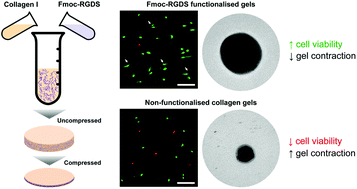
The incorporation of small bioactive peptide motifs within robust hydrogels constitutes a facile procedure to chemically functionalise cell and tissue scaffolds. In this study, a novel approach to utilise Fmoc-linked peptide amphiphiles comprising the bio-functional cell-adhesion RGDS motif within biomimetic collagen gels was developed. The composite scaffolds thus created were shown to maintain the mechanical properties of the collagen gel while presenting additional bio-activity. In particular, these materials enhanced the adhesion and proliferation of viable human corneal stromal fibroblasts by 300% compared to non-functionalised gels. Furthermore, the incorporation of Fmoc-RGDS nanostructures within the collagen matrix significantly suppressed gel shrinkage resulting from the contractile action of encapsulated fibroblasts once activated by serum proteins. These mechanical and biological properties demonstrate that the incorporation of peptide amphiphiles provides a suitable and easy method to circumvent specific biomaterial limitations, such as cell-derived shrinkage, for improved performance in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...