Biodegradable nanoparticles composed of enantiomeric poly(γ-glutamic acid)-graft-poly(lactide) copolymers as vaccine carriers for dominant induction of cellular immunity
Abstract
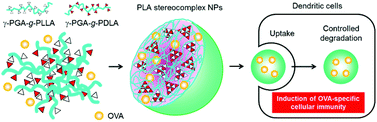
The design of particulate materials with controlled degradation at desired sites is important in applications for drug/vaccine/gene delivery systems. Amphiphilic biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles are promising vaccine delivery carriers due to their ability to stably maintain antigens, provide tailored release kinetics, effectively target, and function as adjuvants. In this study, we report that stereocomplex nanoparticles (SC NPs) composed of enantiomeric poly(γ-glutamic acid)-graft-poly(lactide) (γ-PGA–PLA) copolymers are excellent protein delivery carriers for vaccines that can deliver antigenic proteins to dendritic cells (DCs) and elicit potent immune responses. We prepared ovalbumin (OVA)-encapsulated γ-PGA–PLA SC NPs (OVA-SC NPs) and isomer NPs. These NPs were efficiently taken up by DCs and also affected the intracellular degradation of the encapsulated OVA. The degradation of OVA encapsulated into the SC NPs was attenuated as compared to free OVA and the corresponding isomer NPs. Interestingly, immunization with OVA-SC NPs predominantly induced antigen-specific cellular immunity. The crystalline structure of inner NPs consisting of PLA had a significant impact on the degradation profiles of NPs and the release/degradation behavior of encapsulated antigens and thus the efficiency of immune induction. Our findings suggest that the γ-PGA–PLA SC NPs are suitable for protein-based vaccines that are used to induce cellular immunity, such as for infectious diseases, cancer, allergies and autoimmune diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...