Design and use of silica-containing redox nanoparticles, siRNPs, for high-performance peritoneal dialysis†
Abstract
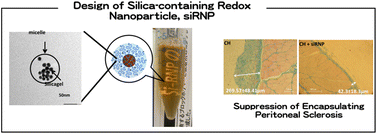
The prevention of encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis (EPS) and the enhancement of dialysis efficiency are two important strategies that can improve the quality of life of patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. We have thus far developed bionanoparticles that effectively scavenge reactive oxygen species (redox nanoparticles; RNPs). The objective of this study was to apply RNPs as a component of dialysate to reduce oxidative stress. Porous silica nanoparticles were combined with RNPs to enhance the effective adsorption capacity of low-molecular weight (LMW) compounds. The silica-containing RNPs (siRNPs) were confirmed to statistically decrease the level of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen in vivo. EPS model rats that underwent an intraperitoneal injection of chlorhexidine gluconate exhibited dysfunction of the peritoneal membrane. siRNP administration did not result in dysfunction of the peritoneal membrane. An LMW nitroxide compound, TEMPOL, also showed a weak peritoneal protective effect, although its efficiency was limited. No blood uptake of siRNPs was observed when they were administered into the peritoneal cavity. However, LMW-TEMPOL diffused into the blood stream, which might have decreased its effective concentration in the peritoneal cavity and led to adverse effects across the entire body. Considering these results, siRNPs are expected to be a new multi-functional nanomaterial for high performance peritoneal dialysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...