Biocompatibility, biodistribution and efficacy of magnetic nanohydrogels in inhibiting growth of tumors in experimental mice models†
Abstract
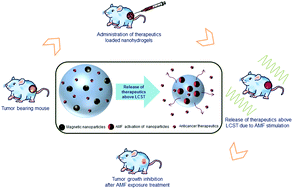
We report in vivo evaluation of a thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-chitosan based magnetic nanohydrogel (MNHG) incorporated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) in mice models with expandible scope for use in localized delivery of chemotherapeutics. Biocompatibility and biodistribution of the MNHG are studied in normal Swiss mice while efficacy in tumor growth inhibition is studied in a subcutaneous fibrosarcoma tumor. The ex vivo time-dependent pattern of accumulated MNHG into vital organs; lung, liver, spleen, kidney and brain collected at 1 h, 48 h, 7 d and 14 d post intravenous administration are investigated using both a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) and inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) method. The doses of MNHG (dose I ∼ 650 and dose II ∼ 325 μg g−1 body wt) used in the study are determined based on induced thermal activation of MNHG under an AC magnetic field (AMF). Fibrosarcoma tumor bearing mice are subjected to hyperthermia with a field of 325 Oe and 265 kHz for 30 min following intratumoral administration of dose I. Tumor size measured at an interval of 72 h for a period of 2 weeks reveals that the NPs mediated therapy decelerated the growth of the transplanted tumor by about three-fold (size, 1545 ± 720 mm3) as compared to the exponential growth of the tumor (size, 4510 ± 735 mm3) in control mice. These results suggest the feasibility of using poly(NIPAAm)-chitosan hydrogels loaded with NPs for combined thermo-chemotherapy where the efficacy may further be improved by temperature dependent release of the drugs from the magneto hydrogels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...