Development of microbial resistant Carbopol nanocomposite hydrogels via a green process
Abstract
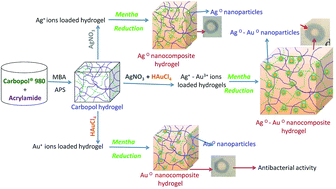
The present scientific research resulted in the development of novel microbial resistant inorganic nanocomposite hydrogels, which can be used as antibacterial agents. They are promising candidates for advanced antimicrobial applications in the field of biomedical science. Novel inorganic nanocomposite hydrogels were developed from Carbopol® 980 NF and acrylamide. Dual-metallic (Ag0–Au0) nanoparticles were prepared (via a green process) by the nucleation of silver and gold salts with mint leaf extract to form a hydrogel network. The Carbopol nanocomposite hydrogels contain (Ag0–Au0) nanoparticles ∼5 ± 3 nm in size, which was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. The developed hydrogels were characterized using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The pure and inorganic nanocomposite hydrogels developed were tested against Bacillus and E. coli, for their antibacterial properties. The results indicate that the inorganic nanocomposites show significantly greater antimicrobial activity than the pure hydrogels. Therefore, novel microbial resistant Carbopol nanocomposite hydrogels can be used as potential candidates for antibacterial applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...