Isothermal haRPA detection of blaCTX-M in bacterial isolates from water samples and comparison with qPCR†
Abstract
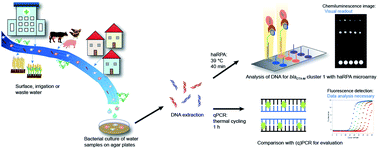
Antibiotic resistant bacteria complicate infection treatment worldwide. Rapid and inexpensive detection of the current occurrence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in surface and irrigation water as well as treated wastewater is essential to minimize exposure and further spread. To reduce cost and analysis time compared to current qPCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction), isothermal nucleic acid amplification tests are promising bioanalytical methods which can be integrated in simplified molecular biological detection systems. This study establishes heterogeneous asymmetric recombinase polymerase amplification (haRPA) for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes in water. After DNA extraction of bacteria cultivated from water, the target DNA for blaCTX-M cluster 1 was amplified at 39 °C for 40 min on a microfluidic DNA chip. The amplified DNA on each spot was quantified by a flow-based chemiluminescence reaction. Even though slightly less sensitive than conventional qPCR, the haRPA method was successful in identifying the blaCTX-M cluster 1 in bacterial isolates with a limit of detection of 0.013 ng μL−1. In a proof-of-principle study, 37 bacterial isolates from environmental water samples were classified according to blaCTX-M cluster 1 occurrence and gave 100% agreement in cross-reference with PCR. Importantly, haRPA allows for a quick in-field monitoring at low incubation temperatures and by an easy visual readout. This study paves the path to establish haRPA as a quick on-site monitoring option for antibiotic resistance gene occurrence without the need for a thermal cycling device or long data processing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...