Phage-mediated double-nanobody sandwich immunoassay for detecting alpha fetal protein in human serum†
Abstract
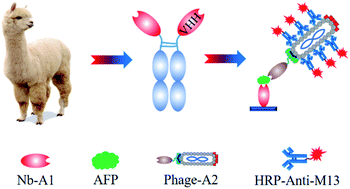
Alpha fetal protein (AFP) is a significant biomarker of liver cancer. Herein we developed a novel phage-mediated double-nanobody sandwich immunoassay (P-ELISA) for sensitive detection of AFP in serum, where the phage displayed the nanobody for antigen recognition and multiple copies of major coat protein pVIII for signal amplification. The expressed nanobody Nb-A1 and the phage-displayed nanobody phage-A2 served as the capture antibody and detection antibody, respectively. Based on the optimal experimental conditions, the P-ELISA has a half maximal saturation concentration of 24.85 ng mL−1 and a limit of detection of 0.237 ng mL−1 for AFP. The P-ELISA is highly selective for AFP and ignorable cross-reactions were observed with other tested cancer biomarkers. After elimination of the matrix effect by 30-fold dilution with 0.5 × PBS, clinical serum samples were analyzed by the P-ELISA. The results correlated well with those of the AFP commercial ELISA kit and the Roche E601 automatic chemiluminescence analyzer. Thus, it showed the potential of the recombinant phage for highly sensitive and selective detection of AFP and provides a novel detection model for the other disease-related biomarkers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...