Glutathione detection in human serum using gold nanoparticle decorated, monodisperse porous silica microspheres in the magnetic form†
Abstract
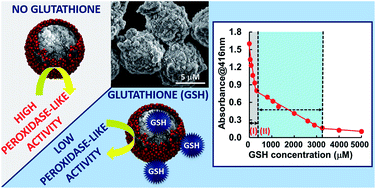
A nanozyme for glutathione (GSH) detection in a broad concentration range was synthesized. GSH is usually detected up to an upper limit of 100 μM using current noble metal nanozymes due to the sharp decrease in the colorimetric response with the increasing GSH concentration. Strong inhibition of colorimetric reactions by GSH adsorbed onto noble metal based nanozymes in the form of non-porous, nanoscale particulate materials dispersed in an aqueous medium is the reason for the sharp decrease in the colorimetric response. In the present study, a new magnetic nanozyme synthesized by immobilization of Au nanoparticles (Au NPs) on magnetic, monodisperse porous silica microspheres (>5 μm) obtained by a “staged-shape templating sol–gel protocol” exhibited peroxidase-like activity up to a GSH concentration of 5000 μM. A more controlled linear decrease in the peroxidase-like activity with a lower slope with respect to that of similar nanozymes was observed with the increasing GSH concentration. The proposed design allowed the GSH detection in a broader concentration range depending on the adsorption of GSH onto the Au NPs immobilized on magnetic, monodisperse porous silica microspheres. A calibration plot allowing the detection of GSH in a broad concentration range up to 3300 μM was obtained using the magnetic nanozyme. The GSH concentration was also determined in human serum by elevating the upper detection range and adjusting the sensitivity of detection via controlling the nanozyme concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...