Benzene-assisted photoionization positive ion mobility spectrometry coupled with a time-resolved introduction for field detecting dimethyl sulfide in seawater†
Abstract
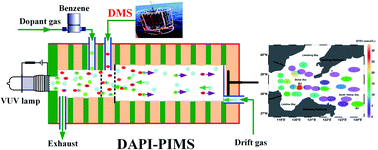
Biogenic dimethyl sulfide (DMS) has attracted widespread attention over several decades due to its potential role in linking ocean biology and climate. The air-to-sea exchange flux, estimated based on marine DMS concentration, offers useful information for evaluating its contribution to climate change. As such, field observation techniques with the characteristics of fast testing speed, portability and easy operation are in demand to accurately monitor the DMS in seawater. In this paper, we proposed a new strategy for the sensitive field measurement of DMS in seawater based on benzene-assisted photoionization positive ion mobility spectrometry (BAPI-PIMS) coupled with a time-resolved introduction. Benzene was employed as a dopant to improve the selectivity by keeping the other sulfur compounds from being ionized, while the two-dimensional data versus drift time and retention time were obtained via an online separating column to eliminate the adverse impact of environmental moisture. Under the optimization conditions, the LODs (S/N = 3) for two product-ion peaks (PIPs) of DMS decreased to 0.081 nmol L−1. Finally, the established method was applied to the lab and ship-board analysis of seawater from the Bohai Sea and the North Yellow Sea in the summer of 2019, and DMS in surface seawater was in the range of 0.11–23.90 nmol L−1 with an average of 9.88 ± 6.96 nmol L−1, indicating the potential for the field detection of marine DMS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...