Probing arsenic trioxide (ATO) treated leukemia cell elasticities using atomic force microscopy†
Abstract
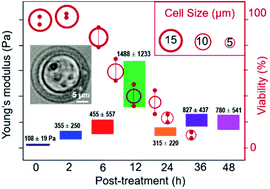
Conventional analytical techniques allow for the diagnosis of leukemia, blood and bone marrow cancers, as well as their classification into the different subtypes. However, a better understanding of the cancer treatment through cell apoptosis staging is still required. Evaluation of the timeline and responses of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells to the arsenic trioxide (ATO) treatment is essential for determining the oral dosage in leukemia prognosis. Here, an Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) indentation approach has been used to evaluate the mechanical responses of cellular responses of APL cells to ATO treatment, alongside well-established cell viability assays, as a novel method to determine the impact of drugs. In addition, cell morphology was quantified to monitor cellular apoptosis. Viability, morphology and elasticity changes of NB4 cells (derived from Human APL patients) were correlated to different time courses of the ATO treatments. Unveiling the relationships among structural, morphological and nanomechanical properties in response to ATO drug treatment promises to pave the way for novel diagnostic tools for drug screening and for a better understanding of the specific physical and biological effects of drugs on diseased cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...