An electrochemical DNA sensor for ultrasensitive detection of ARID1a targeting PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor immunological response†
Abstract
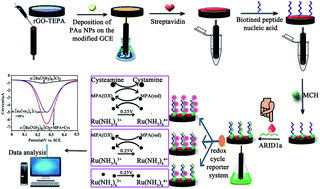
The AT-rich interaction domain 1a (ARID1a) is one of the most commonly mutated genes in cancer. The majority of ARID1a–A5337G mutations makes it a poor therapeutic target. Immunological checkpoint inhibitor therapy targeting PD-1 may successfully reduce the tumor burden of the body. Accordingly, patients are routinely screened for mutations in this gene to determine whether they can benefit from this type of treatment. In this work, we reported a simple and ultrasensitive electrochemical method for ARID1a detection for the first time. In the procedure of the assay, Ru(NH3)63+ is used as the electron acceptor that is electrostatically attracted to peptide nucleic acid (PNA) modified electrodes and new chemical regents of mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) and cysteamine are introduced, which permits Ru(NH3)63+ to be regenerated for multiple redox cycles. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was applied to record electrochemical signals, which increased linearly with the target DNA. Under optimal conditions, the DNA sensors showed a wide linear relationship, from 10 fM to 1 nM, with detection limits of 2.8 fM (S/N = 3). This strategy paves a new way for the determination of ARID1a in patient serum.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...