Exploring asthenozoospermia seminal plasma amino acid disorder based on GC-SIM-MS combined with chemometrics methods†
Abstract
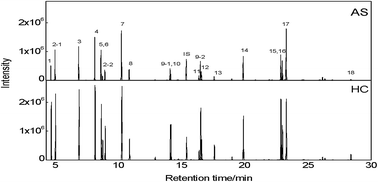
Asthenozoospermia is a common cause of male infertility. Due to the limitation of routine techniques, metabolic alterations associated with the disease and its pathogenesis are still unclear. Metabolic profiling is a powerful tool for studying the metabolic changes, finding potential biomarkers, and revealing the pathophysiological processes of the disease. In this study, amino acid (AA) profiling was used to explore the metabolic disturbance and discover potential biomarkers of asthenozoospermia. Gas chromatography-selective ion monitoring-mass spectrometry (GC-SIM-MS) was used to analyze AAs of seminal plasma from asthenozoospermic men (AS, n = 31) and healthy controls (HCs, n = 21). A supervised orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) method was used to construct the classification model. Furthermore, canonical correlation analysis (CCA) was employed to study the correlation between AAs and clinical parameters. As a result, several amino acids including lysine (Lys), valine (Val) and glycine (Gly) were identified as potential biomarkers. The CCA results showed that rapid progressive motility (a) and vitality are the most important clinical parameters that are closely correlated with AA disorder in AS. Thus more attention should be paid to these parameters in clinical practice for monitoring AA disturbances in AS. The results have demonstrated that metabolic profiling by GC-SIM-MS combined with OPLS-DA and CCA may be a useful tool for discovering AA perturbation of seminal plasma and potential biomarkers for AS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...