Fabrication of an eco-friendly ratiometric fluorescence sensor-modified mesoporous-structured epitope-imprinted polymer for highly selective and sensitive determination of cytochrome c in biological samples†
Abstract
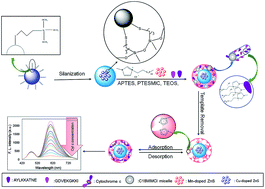
A facile and environmental-friendly strategy was used to prepare ratiometric fluorescence sensor-modified mesoporous-structured epitope-imprinted polymer (QDs@SiO2@EMSiO2) for highly sensitive and selective determination of cytochrome c (Cyt c), using Cu-doped ZnS QDs and Mn-doped ZnS QDs as fluorescent dyes. In this sensor, C-terminal and N-terminal nonapeptides were employed as the template molecules, and C18MIMCl was utilized as a template for mesoporous silica. APTES and PTESMIC were utilized as functional monomers and TEOS was applied as the cross-linker. The as-prepared fluorescence sensor displayed great selectivity and sensitivity by merging ratiometric fluorescence methodology with mesoporous silica materials to create one system. The composite was employed for the recognition of Cyt c, which displayed good linearity in the range from 0.4 nM to 200.0 nM with a detection limit as low as 0.15 nM, which was much lower than those of non-mesoporous and single emission composites. The sensor also exhibited outstanding applicability in complex matrices, which enabled its employment for Cyt c tracing in human serum samples without any pretreatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...