Quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) study of carcinogenicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in atmospheric particulate matter by random forest (RF)†
Abstract
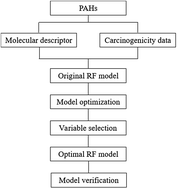
The carcinogenicity or toxicity information of a substance can be quickly and easily obtained by using a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) model. In this study, the carcinogenicity of PAHs was analyzed and predicted by using a random forest (RF) model with the molecular structure information and carcinogenicity data of PAHs. The molecular structure information of 91 PAHs was represented by molecular descriptors (such as structure descriptors, topology descriptors, molecular connectivity index and geometric descriptors) which were calculated by using Dragon5.4 software. The model parameters (ntree and mtry) and input variables were optimized and evaluated with respect to the accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and out-of-bag (OOB) error. Then, based on the optimized model parameters and input variables, the RF, partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and artificial neural network (ANN) models were constructed to predict the carcinogenicity of PAHs. The results show that the classification accuracy, PPV, NPV and modeling time are 0.9333, 0.8889, 1.0000 and 10.40 s for the RF model, respectively, which shows a better predictive ability than the PLS-DA and ANN models for the prediction of the carcinogenicity of PAHs. Therefore, it is demonstrated that RF are a very promising method for the accurate prediction of the carcinogenicity of PAHs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...