Controllable preparation of a reverse-phase/hydrophilic interaction mixed-mode chromatographic stationary phase with adjustable selectivity
Abstract
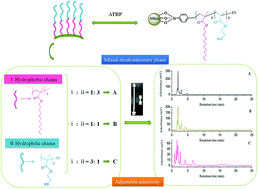
Selectivity is very important for stationary phase applications. However, selectivity is usually quite difficult to adjust once the ligands are fixed. Departing from the reported methods, dodecyl methacrylate (DOMA) and hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) were grafted onto a silica surface via two-step surface initiated-atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP) to synthesize reverse-phase/hydrophilic interaction mixed-mode stationary phases. The grafted amounts of C12 and OH functional groups were controlled by varying the ratios of DOMA to HEMA in the polymerization system. The resulting stationary phases were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis (EA), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometry, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The chromatographic performance and separation selectivity of the packed columns were investigated in different chromatographic modes using a wide range of analytes, including a non-polar benzene series, moderately polar β-agonists as well as organic acids, and strongly polar nucleosides. Exceptionally, the retention of the tested analytes displayed an obvious dependence on the ratio of the two functional monomers in the polymerization. In conclusion, the proposed strategy for the development of a mixed-mode chromatographic stationary phase can provide flexible selectivity by simply tuning the ratios of functional monomers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...