A Fluorescent detection method for copper ions based on a direct redox route and desk study of wax-printed paper-based probes†
Abstract
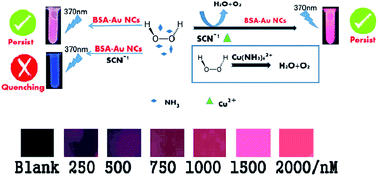
Cu2+ plays an important role in various fundamental physiological processes in organisms. Although Cu2+ probes have been developed, little research has focused on using a direct redox route to quench fluorescence for Cu2+ detection. Herein, a simple, label-free, cost-effective, and sensitive fluorescence method has been developed for Cu2+ detection. In the absence of Cu2+ and presence of NH3+ and SCN−, H2O2 was employed as an oxidant to corrode BSA–Au NCs, resulting in the disappearance of fluorescence. In contrast, in the presence of Cu2+, red fluorescence was maintained because Cu(NH3)62+ can decompose H2O2. Under optimal conditions, good linear correlation between the fluorescent response and Cu2+ concentrations ranging from 5 to 1250 nM was obtained (R2 = 0.9938). Furthermore, this monitoring method has successfully been applied to real urine, tap water, and sorghum extract samples, demonstrating the potential for field applications. Based on this work, we successfully immobilized BSA–Au NCs on wax-printed paper to accomplish real-time field Cu2+ detection. Fluorescence images were captured under UV light (365 nm), and R-values (red value of RGB color model) were analyzed. The obtained linear relationship between the R-value and the Cu2+ concentration demonstrated the potential of this approach. The developed probe also showed satisfactory selectivity and excellent reproducibility. Although previous methods required a masking agent to protect against interference from increasing Hg2+ concentration, Hg2+ and other interfering ions had a near-negligible effect on results in the present work.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...