One-pot synthesis of a fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanosensor for highly selective detection of sulfapyridine in water
Abstract
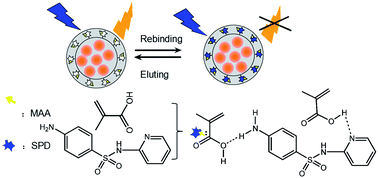
Fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymers (FMIPs) were prepared in a one-pot synthesis using Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots (QDs) as a fluorescent core, sulfapyridine (SPD) as a template, methacrylic acid as a functional monomer, and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a cross-linker for a free-radical polymerization process. These FMIPs could be used for sensing SPD based on fluorescence quenching. As the concentration of Mn2+ in the QDs changed, the fluorescence response of the FMIPs toward SPD also varied. The optimum concentration of Mn2+ for the preparation of Mn-doped ZnS QDs was 2.5 mmol. Under the optimum conditions, the obtained FMIPs showed good binding capacity and high selectivity, and specificity toward SPD. The fluorescence intensity of the FMIPs decreased as the concentration of SPD increased in the range of 0–80 μM, with a detection limit of 0.5 μM. The FMIPs exhibited selectivity towards SPD over its structural analogs sulfanilamide, sulfathiazole, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, sulfamerazine, sulfamethazine, and sulfacetamide. Finally, the FMIPs were successfully applied to detect SPD in tap water samples, and the average recoveries of SPD at three spiking levels ranged from 95.6% to 99.8% with relative standard deviations below 1.4%. This work provides a free-radical polymerization fabrication method for fluorescent MIP sensors, which can be used for rapid recognition and determination of sulfonamides from complex matrices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...