Different molecular weight chitosan derivatives employed for enantiomeric separation†
Abstract
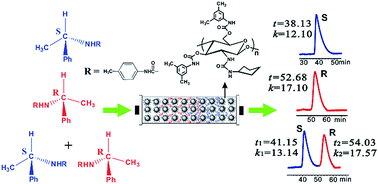
In the present study, four chitosan (cyclopentylurea)s were synthesized from the chitosans with different viscosity-average molecular weights ranging from 1.2 × 105 to 2.1 × 105. The chitosan (cyclopentylurea)s were further derivatized with 3,5-dimethylphenyl isocyanate affording chitosan bis(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate)-(cyclopentylurea)s which were employed as the chiral selectors for enantiomeric separation. Four chiral stationary phases (CSPs) were prepared with the chiral selectors. The enantioseparation capability of the CSPs was evaluated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the tolerability of the chiral selectors against organic solvents was also tested. These CSPs exhibited satisfactory enantioseparation capabilities in comparison with well-known coated-type CSP of cellulose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate), however the capabilities of the four CSPs were not so significantly different. The chiral selectors showed a low swelling capacity in acetone, ethyl acetate and n-hexane/tetrahydrofuran (50/50, v/v), and a medium or high swelling capacity in chloroform and n-hexane/tetrahydrofuran (20/80, v/v). The corresponding CSPs were analyzed with mobile phases using acetone, ethyl acetate and chloroform as additives. The high tolerance to organic solvents reveals that the CSPs have more mobile phase choices for enantiomeric separation. In addition, the influence of one enantiomer of a racemate upon the interaction between the other enantiomer and a chiral selector was studied by HPLC with aid of 1H NMR measurements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...