Effect of sample temperature, pH, and matrix on the percentage protein binding of protein-bound uraemic toxins
Abstract
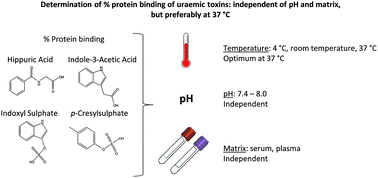
While studying and trying to optimise dialysis clearances of protein-bound uraemic toxins (PBUTs), the percentage protein binding (% PB) may be an important parameter and can be calculated from measured free and total concentrations. Since different parameters may alter this % PB, we investigated whether the ultrafiltration temperature, sample pH, and sample matrix (i.e. serum or plasma) affects the % PB of PBUTs. Pre-dialysis serum and plasma samples were obtained from 10 stable haemodialysis patients. Ultrafiltration was performed at 37 °C for fresh samples and at 4 °C, room temperature, and 37 °C for thawed samples (all n = 10). Total and free serum/plasma concentrations of hippuric acid, indole-3-acetic acid, indoxyl sulphate, and p-cresylsulphate were simultaneously measured by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and fluorescence detection. No differences in % PB were found between fresh and thawed samples at 37 °C or between serum and plasma samples prepared at the same temperatures. However, in both serum and plasma samples, the free concentration increased with increasing ultrafiltration temperatures and resulted in a decrease in % PB from 4 °C to 37 °C. In conclusion, the % PB of PBUTs can be determined in both thawed serum and plasma samples and ultrafiltration should be performed at 37 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...