Demonstration of a tailorable and PCR-free detection of Enterococcus DNA isolated from soil samples†
Abstract
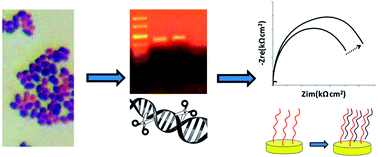
Bacteria detection is crucial for water and environmental monitoring. The challenge in this sector is to have a method specific to a range of pathogens of interest, but not too specific to each strain, so that the method can be used to screen a family of species. In this report we demonstrate a new approach which combines isolation of DNA and label-free detection by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The new approach is shown to be effective with or without using the PCR. The target DNA, common to all Enterococcus species, has been successfully isolated from soil samples, cut by using restriction enzymes and detected to give a positive response.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...