A review of analytical techniques for quantifying microplastics in sediments
Abstract
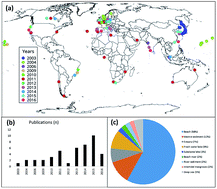
In this review the analytical techniques for measuring microplastics in sediment have been evaluated. Four primary areas of the analytical process have been identified that include (1) sampling, (2) extraction, (3) quantitation and (4) quality assurance/quality control (QAQC). Each of those sections have their own subject specific challenges and require further method development and harmonisation. The most common approach to extracting microplastics from sediments is density separation. Following extraction, visual counting with an optical microscope is the most common technique for quantifying microplastics; a technique that is labour intensive and prone to human error. Spectroscopy (FTIR; Raman) are the most commonly applied techniques for identifying polymers collected through visual sorting. Improvements and harmonisation on size fractions, sampling approaches, extraction protocols and units for reporting plastic abundance would aid comparison of data generated by different research teams. Further, we advocate the development of strong QAQC procedures to be adopted like other fields of analytical chemistry. Finally, inter-laboratory proficiency testing is recommended to give an indication of the variation and reliability in measurements reported in the scientific literature that may be under- or overestimations of environmental burdens.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Analytical Methods 2017 Most Downloaded Articles and Microplastics in the environment


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...