Sensor array optimization and discrimination of apple juices according to variety by an electronic nose
Abstract
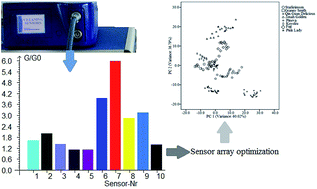
An electronic nose (PEN3) containing 10 metal oxide semiconductor type chemical sensors (W1C, W5S, W3C, W6S, W5C, W1S, W1W, W2S, W2W and W3S) was used to discriminate between eight varieties of apple juice. Sensor array optimization was carried out to eliminate irrelevant, redundant information and improve discrimination accuracy. Traditional ANOVA and loading analysis methods and the Wilks statistics method were conducted and sensors sensitive to aroma compounds were selected to optimize the sensor array. Three optimized sensor sets were obtained. PCA, k-means clustering and SVM were proposed to analyze the original and optimized sensor signals. An exploratory overview using the PCA-based pattern showed that optimized set 2 W5S, W5C, W1W and W3S obtained using the Wilks statistics method performed best. The Wilks statistics method was proven to be a useful tool for sensor array optimization by weighing up the sensors' discriminatory ability. This result was further demonstrated using k-means clustering analysis. The SVM method achieved better discrimination performance in comparison with the PCA-based pattern. SVM revealed satisfactory discrimination of apple juices, provided a 100% success training rate and a 98.33–100% success testing rate. The optimization sensor array was demonstrated to be able to improve the discriminatory performance of EN. The results obtained indicated that EN can be successfully applied to apple juice discrimination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...