High-throughput sialylation measurement using lectins on an Octet platform for clone screening
Abstract
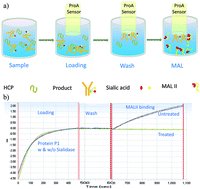
A high-throughput method to quantify sialic acids was developed on a ForteBio Octet QK384 platform to support cell-line development. The high-throughput sialylation analysis method using the ForteBio Octet (HTFBS) is based on the binding rate of Maackia amurensis lectin II (MALII) to (α-2,3)-linked sialic acids of proteins bound to Protein-A sensors. The HTFBS method can specifically quantify the sialylation levels of secreted proteins in crude cell culture samples and does not require purified samples. Using this method, thirty crude cell culture samples can be analyzed for titers and sialylation in 60 minutes. In a comparison study between the HTFBS method and HPLC method, a linear correlation was observed between the MALII binding rate obtained by using the ForteBio Octet QK384 and the total sialic acid content obtained by HPLC for samples in the sialic acid content range of 5–24 mol mol−1. The MALII binding rate was consistent for samples with titers between 6.25 and 100 μg mL−1. The HTFBS method is robust and the effect of protein concentration is negligible on the MALII binding rate for samples between 6.25 and 100 μg mL−1. The HTFBS method was successfully applied to the cell-line development platform for screening highly sialylated clones. The current HTFBS method can quantify sialylation levels in crude samples and can readily be used to accelerate cell line development for producing therapeutic proteins with desired product quality.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...