Simultaneous and differential determination of drugs and metabolites using the same antibody: difloxacin and sarafloxacin case
Abstract
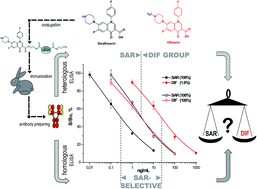
To differentiate the close structurally related fluoroquinolones (FQs) difloxacin (DIF) and its active metabolite/degradant sarafloxacin (SAR) in animal tissues, rabbit polyclonal antibodies against SAR conjugated to ethylenediamine-modified BSA were prepared. Using the same antibody two indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) formats with different specificities, for SAR-selective and SAR/DIF-group determination, were constructed. Depending on the coated gelatin–SAR antigens which were prepared by active ester or formaldehyde condensation methods, the cross-reactivity of DIF changed from 1.9% to 100%, and remained <1% for the other FQs. The limit of detection, half-inhibition concentration (IC50), and dynamic range (IC20–IC80) for the SAR-selective ELISA were found to be 0.018, 0.38, and 0.037–4.43 ng mL−1, respectively, and were 0.18, 2.8, and 0.3–30 ng mL−1, respectively, for SAR and DIF as equal analytes in group assay. An approach based on the parallel analysis of samples in both tests allowed the differential detection of SAR and DIF in chicken and turkey muscles. The recovery from fortified tissue samples ranged from 70 to 118% and confirmed the suitability of the developed screening test for measuring and differentiating these antibiotics at their MRL level in food matrices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...