A greener flow injection method based on a LWCC for the screening of tetracycline antibiotics in bovine milk samples†
Abstract
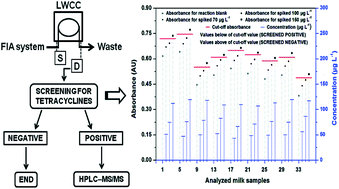
An easy and greener flow injection method was developed for the spectrophotometric screening of tetracycline antibiotic residues in bovine milk. The combined benefits of the use of a detection system based on a liquid waveguide capillary cell (LWCC) and stop-flow (60 s) conditions significantly enhanced (45.6-fold) the analytical sensitivity. The determination is based on the formation of tetracycline azo derivatives (λmax = 435 nm) from diazotized p-sulfanilic acid, in a slightly alkaline medium. The analytical conditions were optimized by multivariate analysis, using a fractional factorial design. The linear range was 50–400 μg L−1, and the limits of detection and quantification were in the ranges 8.6–12.2 μg L−1 and 28.8–40.7 μg L−1, respectively. The applicability of the LWCC-based method was successfully tested using fortified milk samples that were only submitted to a prior acid treatment. The screening provided a quick response, enabling the determination of whether the tetracyclines were above or below the limit established by legislation (100 μg L−1). The positive samples were also analyzed by an AOAC Official Method, and the results obtained with the two methods were in good agreement. Additionally, the presence of tetracycline residues was confirmed using an HPLC-MS/MS reference analytical procedure. The excellent performance of the new screening method makes it suitable for use in the quality control of bovine milk in the food industry, aiming at consumer protection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...