A new green switchable hydrophobic–hydrophilic transition dispersive solid–liquid microextraction of selenium in water samples
Abstract
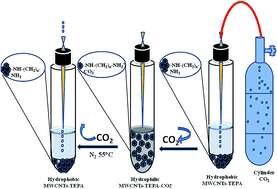
A novel switchable hydrophobic–hydrophilic transition dispersive solid–liquid microextraction (SHT-DSLME) method has been used for the first time as a dispersive/extractive method for the removal of total selenium from real samples. Tetraethylenepentamine modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-TEPA) were synthesized and employed as an adsorbent for the removal and analysis of total inorganic selenium by SHT-DSLME coupled with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS). In this study, the hydrophobic–hydrophilic transition of MWCNTs-TEPA was achieved by exposing them to a green, inexpensive, non-hazardous and non-accumulating antisolvent trigger: CO2. The switching phenomena of functionalized MWCNTs from hydrophobic to hydrophilic were confirmed using FTIR spectrophotometry and SEM measurements. Under optimized experimental conditions, the enhancement factor (EF) and limit of detection (LOD) were found to be 72 and 0.015 μg L−1, respectively for selenium. Validation of the developed method was carried out by selenium determination using water for trace elements (TM-28.3) as a certified reference material and the results were found to be in good agreement with the certified values. The proposed novel method was then successfully applied for the determination of selenium in real water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...