Digital image colorimetry coupled with a multichannel membrane filtration-enrichment technique to detect low concentration dyes†
Abstract
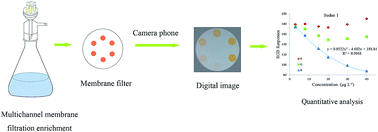
The digital image colorimetry technique was combined with the multichannel membrane filtration-enrichment technique proposed in our previous study to increase its sensitivity. With our multichannel device, six solutions including standard and test samples were enriched and distributed evenly in a circle form on one membrane filter. A digital image of the membrane filter was taken utilizing a mobile phone equipped with a digital camera after filtration. Then the RGB responses for each sample spot were extracted from different regions of the same picture using Adobe Photoshop. The obtained RGB responses (value of the blue component, B) could be utilized directly for quantitative analysis when the picture was taken under a uniform illumination. In addition, the total intensity I (I = R + G + B) was used to minimize the effect of the illumination to the RGB responses, so that the conditions for taking pictures can be softened to a casual environment. A case study was carried out to assess this method utilizing the carcinogenic dyes, Sudan I, Chrysoidine G, Auramine O and Acid orange 7 as model analytes. Under the optimal conditions, there was a quadratic function relationship between the negative value of B/I and the concentration in the concentration range of 3–40 μg L−1 with the squared correlation coefficient (R2) for the four dyes all being above 0.9950. Linear calibration curves were achieved only at a low concentration level and the corresponding limit of detections (LODs) were 1.03 μg L−1 for Sudan I, 3.0 μg L−1 for Chrysoidine G, 2.11 μg L−1 for Acid orange 7, and 0.65 μg L−1 for Auramine O. For each dye, good repeatability was achieved with relative standard deviation (RSD) values all below 3.8%. The results obtained from digital image colorimetry were similar to those obtained from spectral analysis, which proved the accuracy of this method. And the presented method was successfully employed to quantify Sudan I and Acid orange 7 in candy samples, and Chrysoidine G and Auramine O in soft drink samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...