Simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple antibiotic residues in milk based on aptamers and quantum dots†
Abstract
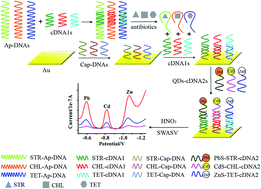
A sensitive simultaneous detection of streptomycin (STR), chloramphenicol (CHL) and tetracycline (TET) residues was achieved based on aptamers and quantum dot (QD) tags. Three complementary DNA1 sequences (cDNA1s) were first designed, which are not only complementary to corresponding aptamer DNAs (Ap-DNAs) specific for STR, CHL and TET, but also complementary to part of capture DNAs (Cap-DNAs) and part of complementary DNA2s (cDNA2s), respectively. cDNA1s initially hybridize with corresponding Ap-DNAs to form duplex DNAs. However, when the target antibiotics are present, STR, CHL and TET can bind with their Ap-DNAs specifically with higher affinity, which leads to the release of cDNA1s. Then the liberated cDNA1s hybridize with corresponding Cap-DNAs which are immobilized on the surface of a gold electrode by self-assembly. After that, the prepared PbS, CdS and ZnS QDs-tagged cDNA2s further hybridize with the other ends of corresponding cDNA1s on the electrode surface. The captured QDs yield distinct electrochemical signals after acid dissolution, which reflect the type and concentration of target antibiotics. Due to the inherent amplification feature of QD tags, the low detection limits for STR, CHL and TET reached 10 nM, 5 nM and 20 nM, respectively. In addition, the established assay was applied in the detection of STR, CHL and TET residues in milk samples and showed similar response ranges.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...