Using fluoro modified RNA aptamers as affinity ligands on magnetic beads for sensitive thrombin detection through affinity capture and thrombin catalysis†
Abstract
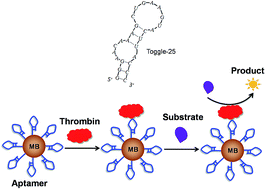
Many RNA aptamers against a variety of targets have been selected, and some of the RNA aptamers can have better binding affinity than DNA aptamers. The application of RNA aptamers against thrombin in bio-analysis previously did not attract enough attention due to the high cost in synthesis and poor stability of RNA aptamers, compared with the wide use of DNA aptamers. Here we present a sensitive and specific assay for thrombin by using a nuclease-resistant fluoro (F) modified RNA aptamer (Toggle-25) as an affinity ligand on magnetic beads to explore the capability of this RNA aptamer for thrombin detection and expand its application. This RNA aptamer had high binding affinity and good stability. The RNA aptamers were immobilized on the magnetic beads to selectively capture thrombin, and then thrombin cleaved fluorogenic or chromogenic peptide substrates. The measurement of the generated product allowed the final detection of thrombin. This assay reached a detection limit of 10 fM when a fluorogenic substrate was used. Thrombin could be successfully detected in diluted human serum. This work shows that the applied RNA aptamer Toggle-25 is a good alternative to DNA aptamers of thrombin as an affinity ligand, and it can be used in developing assays for thrombin. Other assays for thrombin can be expected by using this RNA aptamer with a different detection format.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...