Determination of trace levels of iron in serum samples of hepatitis B and C patients using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction
Abstract
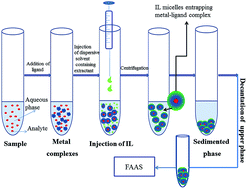
An environmentally friendly ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (IL-DLLμE) method was developed for the preconcentration of trace levels of iron (Fe) in serum samples of hepatitis B and C patients, prior to its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The procedure was based on complexation of iron with a chelating reagent, 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine), whereas an ionic liquid, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [C4MIM][PF6], and ethanol were chosen as extracting and dispersive solvents, respectively. The factors affecting the efficiency of IL-DLLμE, such as the amount of IL, pH, centrifugation time and ligand concentration, were investigated in detail. The resulting data indicated that the coexisting cations and anions ions had no apparent influence on determination of Fe at trace levels. Under optimal experimental conditions, the enhancement factor and the limit of detection were 59.1 and 1.29 μg L−1, respectively. The relative standard deviation for five replicate determinations of Fe at 50 μg L−1 was calculated to be <5.0%. The developed method was validated by determining Fe in a certified reference material of serum. The proposed method can be successfully used for the enrichment of Fe in acid digested serum samples of female hepatitis B and C patients.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...