Mass spectrometry-based lipidomics analysis using methyl tert-butyl ether extraction in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues†
Abstract
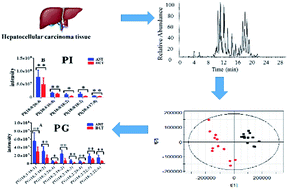
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers in human beings and not well treated. Due to its blurred biomarkers, lipidomics can be considered as a new diagnostic tool. In this study, mass spectrometry-based lipidomics analysis coupled with multivariate statistical analysis was applied to profile twelve pairs of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues (HCT) and matched adjacent non-tumour tissues (ANT). As a result, perturbation of lipid biosynthesis was observed in HCT compared to ANT. Lipid species were profiled and 28 significant lipids were identified based on high resolution mass spectrometry with mass error less than 3 ppm, covering phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylinositol (PI), sphingomyelin (SM) and triglyceride (TG). The high mass accuracy as well as the tandem MS (MS/MS) technique provides high confidence of lipid identification. Interestingly, decreased PGs and PIs were observed in this study, indicating that lipolysis of PGs and PIs might play a crucial role in HCC development. The results indicated that mass spectrometry-based lipidomics analysis could serve as an effective means to diagnose canceration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...