A sensitive cytosensor for sialic acid assay based on dual signal amplification by functionalized carbon nanospheres and enzymatically produced polyaniline
Abstract
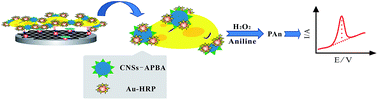
It is widely acknowledged that sialic acid (SA) overexpression on cell surfaces has been thought to be a characteristic feature associated with many malignant diseases. In this paper, we report a new strategy for SA expression evaluation and electrochemical cytosensing of living cells. High selectivity and sensitivity were achieved by combining 3-aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) modified carbon nanospheres (CNS-APBA) for SA recognition and horseradish peroxidases (HRP) decorated on gold nanoparticles (Au-HRP NPs) for signal amplification. The HRP labels can effectively catalyze the oxidation of aniline in the presence of H2O2 to form polyaniline (PAn). The relatively positive detection potential range for PAn completely excluded the conventional interference from dissolved oxygen. Based on the dual signal amplification by functionalized carbon nanospheres and enzymatically produced polyaniline, the designed cytosensor can be used for SA evaluation on cancer cell surfaces and highly sensitive cell detection with a wide calibration range (from 5.0 × 102 to 1.0 × 106 cells per mL for MCF-7 cells and from 1.0 × 103 to 1.0 × 106 cells per mL for BGC-823 cells) and a low detection limit (25 cells per mL for MCF-7 cells and 800 cells per mL for BGC-823 cells). This strategy provides a valuable tool for the evaluation of sialic acid on cancer cells and great potency for cancer study.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...