Quantification and characterization of naphthenic acids in soils from oil exploration areas in China by GC/MS†
Abstract
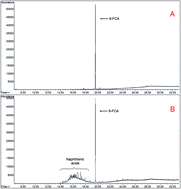
Naphthenic acids (NAs) are a toxic complex mixture of carboxylic acids occurring naturally in petroleum. Due to the serious potential risks of NAs towards terrestrial ecology during crude oil exploration and production processes, and the lack of efficient methodologies for extraction and analysis of these compounds, the goal of this study is to detail the development of a routine method for extraction, and quantitative and qualitative analysis of NAs in oil contaminated soils. Solid phase extraction using a MAX cartridge was employed in combination with GC/MS. Ethyl acetate with 2% formic acid used as an elution solvent showed the best recoveries of NAs (98.36–112.35%). The total NA concentration and NA profiles of oil contaminated soil samples from 4 oil fields in China were examined. High concentrations of NAs (maximum, 132.91 mg kg−1) were detected in soils, which implied toxic and estrogenic risks for human and terrestrial organisms. Different profiles of NA mixtures were observed in soils from 4 different oil fields, and evaporation and biodegradation could influence the compounds of NAs. The authors present the first feasible method for analysis of NAs in soil.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...