Hollow fiber supported liquid-phase microextraction combined with maltodextrin-modified capillary electrophoresis for the determination of citalopram enantiomers in urine samples†
Abstract
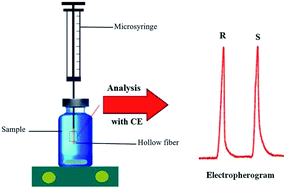
A simple and highly sensitive method that involves three-phase hollow fiber supported liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME) coupled with maltodextrin (MD)-modified capillary electrophoresis (CE) was successfully developed for the separation and determination of trace concentrations of citalopram (CIT) enantiomers in urine samples. The results of the enantioseparation with CE showed that the R-enantiomer of CIT migrated faster than the S-enantiomer. The analyte was extracted into 1-octanol that was immobilized in the wall pores of a porous hollow fiber from 4.0 mL of aqueous sample, at pH 12.5 (donor phase), and was back extracted into the acceptor phase (pH 2.2) located in the lumen of the hollow fiber. A Box–Behnken design (BBD) and the response surface methodology (RSM) were used for the optimization of different parameters for the extraction efficiency. The limits of quantification and detection for both R-CIT and S-CIT were 10 and 30 ng mL−1, respectively. The method was reproducible so that the intra- and inter-day RSDs% (n = 5) were less than 6.9%. Finally, this method was successfully applied to determine the concentration of CIT enantiomers in real urine samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...