A colorimetric sensor for pH utilizing a quinoline derivative
Abstract
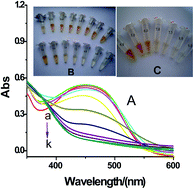
A simple sensor utilizing a simple aminoquinoline derivative (5-(quinolin-8-yliminol) pentanal, QYP) has been successfully developed for the naked-eye colorimetric assay of pH. The QYP compound presents strong solvatochromism due to the solute–solvent interaction, and it is sensitive to a pH change in the solution. The color of the solution changes from orange to colorless upon increasing the pH value, which is well consistent with the corresponding UV/vis absorbance variation. UV absorbance has a direct linear relationship with the pH values in the range of 4.0 to 8.0 in phosphate-buffered saline, and the corresponding color variation could be distinguished readily by the naked eye.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...