Identification of materials' binding peptide sequences guided by a MALDI-ToF MS depletion assay†
Abstract
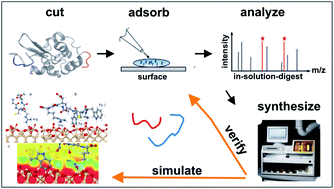
We introduce a novel technique for an initial identification of peptide sequences that specifically bind to material surfaces based on the matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF MS) depletion method. The technique relies upon time-resolved, sensitive measurements of the MALDI-ToF MS peak signals acquired from a solution containing several peptides placed in contact with an inorganic surface, in our case amorphous SiO2. Large errors intrinsic in the MALDI-ToF MS spectral analysis and uncertainties arising from the adsorption behaviour of peptide mixtures limit the predictive power of the method. However, when combined with other characterisation and modelling techniques, such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) and Molecular Dynamics (MD), it can be used as a guide to identify novel material-binding peptide sequences, such as TPGSR for SiO2. The strategy presented in this work may have an impact on the design and synthesis of novel hybrid biomaterials based on the biomolecular recognition of inorganic surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...