Applications of a confined DART (direct analysis in real time) ion source for online in vivo analysis of human breath
Abstract
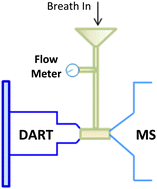
Human breath is composed of many volatile metabolites that can potentially provide information about a person's health status. A sensitive assay to identify these volatile organic compounds as biomarkers is ideal and important for early detection of many diseases. However, the diagnosis through online breath analysis based on mass spectrometry is difficult due to the low concentration of pertinent compounds in breath. The DART (direct analysis in real time) ion source is a novel atmospheric pressure ionization technique, which can efficiently ionize gaseous, liquid and solid samples with high throughput. A major problem in analysis of gaseous samples is its poor detection sensitivity due to open-air sampling. Recently, a confined DART ion source (cDART) was developed, where the plasma generated by the atmospheric pressure glow discharge ionizes gas-phase molecules in a Tee-shaped flow tube instead of open air. It leads to a significant increase of the ionization efficiency of gaseous samples. In this study, the cDART source was modified and applied in online analysis of exhaled breath. The limit of detection of the improved cDART source was determined to be at the level of low ppb. The cDART source was used in the real-time monitoring of an oral anesthetic drug. The concentration variations of two active ingredients in exhaled breath, menthol and benzocaine, and their metabolites with time were obtained. The results show that the cDART ion source is a powerful analytical tool to provide high sensitivity and high throughput analysis for volatile organic compounds in human breath, and can find potential applications in clinical diagnosis and therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...