Cell-free hemoglobin is a marker of systemic inflammation in mouse models of sepsis: a Raman spectroscopic study†
Abstract
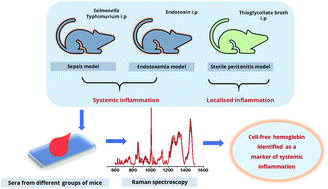
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by heightened host immune responses post infection. Despite intensive research, most of the existing diagnostic methods remain non-specific, labour-intensive, time-consuming or are not sensitive enough for rapid and timely diagnosis of the onset and progression of sepsis. The present work was undertaken to explore the potential of Raman spectroscopy to identify the biomarkers of sepsis in a label-free and minimally invasive manner using different mouse models of inflammation. The sera of BALB/c mice infected with Salmonella Typhimurium reveal extensive hemolysis, as indicated by the Raman bands that are characteristic of the porphyrin ring of hemoglobin (668, 743, 1050, 1253 and 1397 cm−1) which increase in a kinetic manner. These markers are also observed in a lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock model, but not in a thioglycollate-induced sterile peritonitis model. These data demonstrate that hemolysis is a signature of systemic, but not localised, inflammation. To further validate our observations, sepsis was induced in the nitric oxide synthase 2 (Nos2−/−) deficient strain which is more sensitive to infection. Interestingly, Nos2−/− mice exhibit a higher degree of hemolysis than C57BL/6 mice. Sepsis-induced hemolysis was also confirmed using resonance Raman spectroscopy with 442 nm excitation which demonstrated a pronounced increase in the resonant Raman bands at 670 and 1350 cm−1 in sera of the infected mice. This is the first study to identify inflammation-induced hemolysis in mouse models of sepsis using Raman spectral signatures for hemoglobin. The possible implications of this method in detecting hemolysis in different inflammatory pathologies, such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...