Rapid capture of biomolecules from blood via stimuli-responsive elastomeric particles for acoustofluidic separation†
Abstract
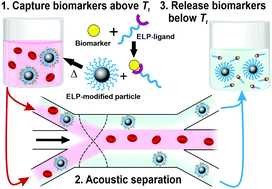
The detection of biomarkers in blood often requires extensive and time-consuming sample preparation to remove blood cells and concentrate the biomarker(s) of interest. We demonstrate proof-of-concept for a chip-based, acoustofluidic method that enables the rapid capture and isolation of a model protein biomarker (i.e., streptavidin) from blood for off-chip quantification. Our approach makes use of two key components – namely, soluble, thermally responsive polypeptides fused to ligands for the homogeneous capture of biomarkers from whole blood and silicone microparticles functionalized with similar, tethered, thermally responsive polypeptides. When the two components are mixed together and subjected to a mild thermal trigger, the thermally responsive moieties undergo a phase transition, causing the untethered (soluble) polypeptides to co-aggregate with the particle-bound polypeptides. The mixture is then diluted with warm buffer and injected into a microfluidic channel supporting a bulk acoustic standing wave. The biomarker-bearing particles migrate to the pressure antinodes, whereas blood cells migrate to the pressure node, leading to rapid separation with efficiencies exceeding 90% in a single pass. The biomarker-bearing particles can then be analyzed via flow cytometry, with a limit of detection of 0.75 nM for streptavidin spiked in blood plasma. Finally, by cooling the solution below the solubility temperature of the polypeptides, greater than 75% of the streptavidin is released from the microparticles, offering a unique approach for downstream analysis (e.g., sequencing or structural analysis). Overall, this methodology has promise for the detection, enrichment and analysis of some biomarkers from blood and other complex biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
