Extracellular pH-manipulated in situ reconfiguration of aptamer functionalized DNA monomer enables specifically improved affinity, detection and drug delivery†
Abstract
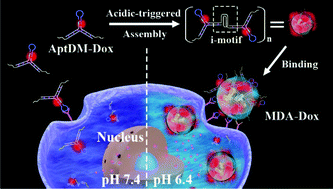
Aptamers are promising in cancer diagnosis and therapy, but their poor affinity under physiological conditions is a challenge. In view of the acidic microenvironment of solid tumors, we herein developed an extracellular pH-manipulated multivalent approach to exclusively improve the affinity to target cells at physiological temperature. Specifically, an aptamer based DNA monomer (AptDM) with split i-motif fragments overhanging was rationally designed, it possessed pH-responsiveness and doxorubicin loading capacity. At neutral pH, AptDMs existed as well dispersed small units, showing weakly undesired binding and internalization. In acidic extracellular conditions, AptDMs tended to crosslink of each other into multivalent DNA assemblies (MDAs) via formation of an intermolecular i-motif structure. Due to the multivalent effect, the resulting MDAs showed greatly enhanced affinity (Kd = 9.96 ± 1.06 nM) and stable binding ability at 37 °C, thus allowing highly sensitive diagnosis, efficient drug delivery, and improved inhibition to target tumor cells, but decreased cytotoxicity to nontarget cells. It is believed that this multivalent approach may boost the development of novel aptamer functionalized nanodevices for clinical validation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...