Isothermal cross-boosting extension–nicking reaction mediated exponential signal amplification for ultrasensitive detection of polynucleotide kinase†
Abstract
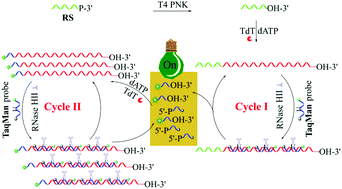
A novel nucleic acid-based isothermal signal amplification strategy, named cross-boosting extension–nicking reaction (CBENR) is developed and successfully used for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of polynucleotide kinase (PNK) activity. Only two simple oligonucleotides (recognition substrate (RS) and TaqMan probe) are applied to construct the PNK-sensing platform. In the presence of PNK, the 3′-phosphate end of RS will be converted to the 3′-hydroxyl one, and then extended to a long poly-adenine (poly-A) sequence under the catalysis of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT). The poly-A sequence provides multiple binding sites for the TaqMan probe to form multiple DNA duplexes. Subsequently, ribonuclease HII (RNase HII) cuts the TaqMan probe into two parts at the pre-set uracil site, generating a fluorescence signal and providing new substrates for TdT elongation. The TdT-catalyzed substrate extension and RNase HII-catalyzed probe nicking are boosted by each other, resulting in persistent enlargement of these two reactions and thus giving ultrahigh signal amplification efficiency. Utilizing the CBENR-based PNK sensor, ultrasensitive detection of PNK activity was achieved with a detection limit as low as 3.0 × 10−6 U mL−1. Quantification of endogenous PNK activity at the single-cell level and the screening/evaluation of PNK inhibitors were also achieved.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...